Accounting Differences Across Countries

One such cornerstone in the accounting profession is the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Understanding GAAP is is gaap used internationally crucial for accountants, business owners, financial analysts, and anyone involved in preparing and analyzing financial statements. The Financial Accounting Standards Board defines the accounting standards for the US. Collectively, these standards form what are called the generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). The GAAP outlines the procedures and practices that must be followed by public companies in the US, including what financial statements and other information must be recorded and reported. Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) is the accounting standard set by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) for the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the United States.

2: International Accounting Standards
As multinational companies expand, the demand for a single set of accounting standards becomes more pressing. This convergence aims to enhance comparability, transparency, and efficiency in financial markets worldwide. The treatment of leases under IFRS and GAAP presents notable differences that impact financial statements and the perception of a company’s financial health. IFRS 16 requires lessees to recognize nearly all leases on the balance sheet, which includes both finance and operating leases.
Income Statements in Finance and Accounting: A Complete…

Four of the examples provided in paragraph 10 are similar to the four criteria for lease classification in SFAS 13. GAAP, IAS 17 indicates that if the lease term is for the major part of the asset’s economic life, it normally would be classified as a capital lease. One manifestation of this flexibility is that Dutch and British law allow companies to write up assets to higher market values, but in Germany this is strictly forbidden. Notwithstanding this flexibility, implementation of the directives into local law caused extensive change in accounting practice in several countries. Large numbers of German and Swiss multinational companies (including Deutsche Bank, Bayer, and Nestle), in particular, took advantage of this option. The two classes of accounting reflected in Exhibit 11.6 differed significantly on 66 of the 100 financial reporting practices examined.
- The cost principle states that assets must be recorded at their original purchase price less depreciation and impairment charges.
- The publication of a final IAS required approval of at least 11 of the 14 board members.
- Efforts to converge GAAP and IFRS have been ongoing for many years, spearheaded by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB).
- These principles outline the rules and guidelines that companies must follow when preparing and presenting their financial statements.
- The IFRS International Financial Reporting Standards are the most generally used accounting regulations outside the United States.
- IFRS are written in English and therefore must be translated into other languages for use by non- English-speaking accountants.
Inventory Valuation
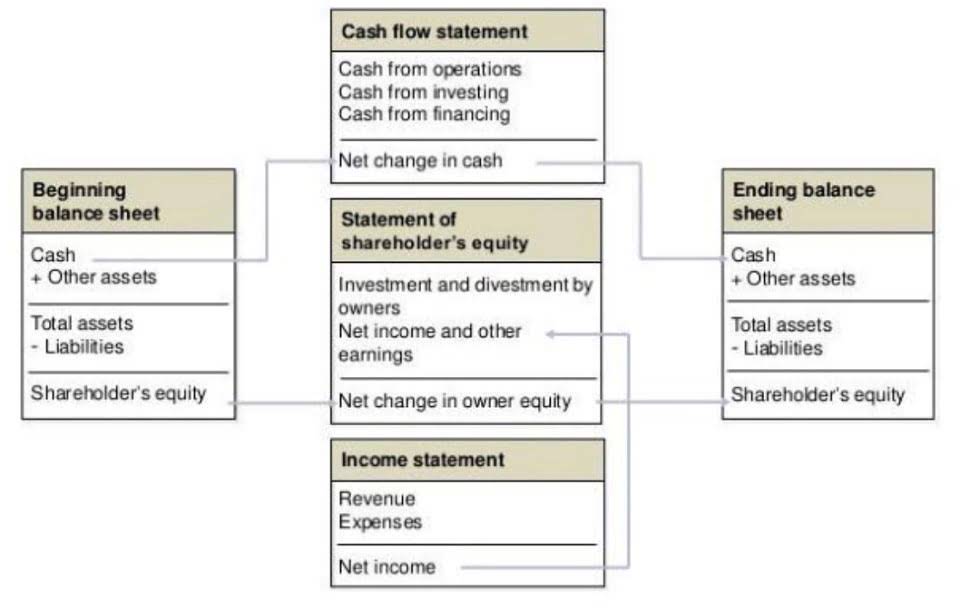
This section will provide an overview of key GAAP fundamentals, principles, and how GAAP compares to International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Most international accountants would agree that understanding US GAAP can be incredibly challenging. Enroll in GAAP Standards in Finance and Accounting training at BMC Training and gain the expertise needed to ensure compliance and financial accuracy.
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest accounting insights and updates
Companies face enormous pressure to engage skilled accountants since the costs of manipulating records or providing insufficient accounting services are considerable. Without that trust, we may see fewer transactions, leading to higher transaction costs and a weaker economy. GAAP also assists investors in analyzing companies by making “apples-to-apples” comparisons between one company and another easier. The IFRS International Financial Reporting Standards are the most generally used accounting regulations outside the United States. Similarly, balance sheets under GAAP must present current Retail Accounting accounts before non-current, while internationally, non-current liabilities are often listed first. International accounting differs from US accounting when it comes to long-lived assets.

Some Key Differences Between IFRS and GAAP
- Understanding these nuances is crucial for stakeholders who rely on financial statements for decision-making.
- The collaboration between FASB and SEC and the implementation of critical standards fortify the integrity of financial reporting in the United States.
- GAAP encompasses a wide range of accounting activities, including revenue recognition, balance sheet item classification, and materiality.
- If you’re new to the balance sheet, understanding each of its components can seem like an overwhelming and complicated ordeal.
- When employing an accountant, retain a finance lawyer to assist you in vetting competent candidates.
The establishment of regulatory bodies, such as the SEC and the FASB, has played a significant role in developing and enforcing GAAP, ensuring consistency, reliability, and transparency in financial reporting. In summary, GAAP exists to promote what are retained earnings standardization, reliability, transparency, and comparability in financial reporting. It plays a crucial role in facilitating decision-making, ensuring compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, and building trust among stakeholders in the financial markets. GAAP provides a set of standardized accounting principle that enable businesses and organizations to consistently prepare and present their financial statements.